Promoting Recycling and Waste Management
India faces significant challenges when it comes to managing its solid waste. The country generates approximately 62 million tonnes of municipal solid waste per year, and a large proportion of this waste is dry waste. Dry waste includes items such as paper, cardboard, plastic, glass, and metal that do not decompose easily.
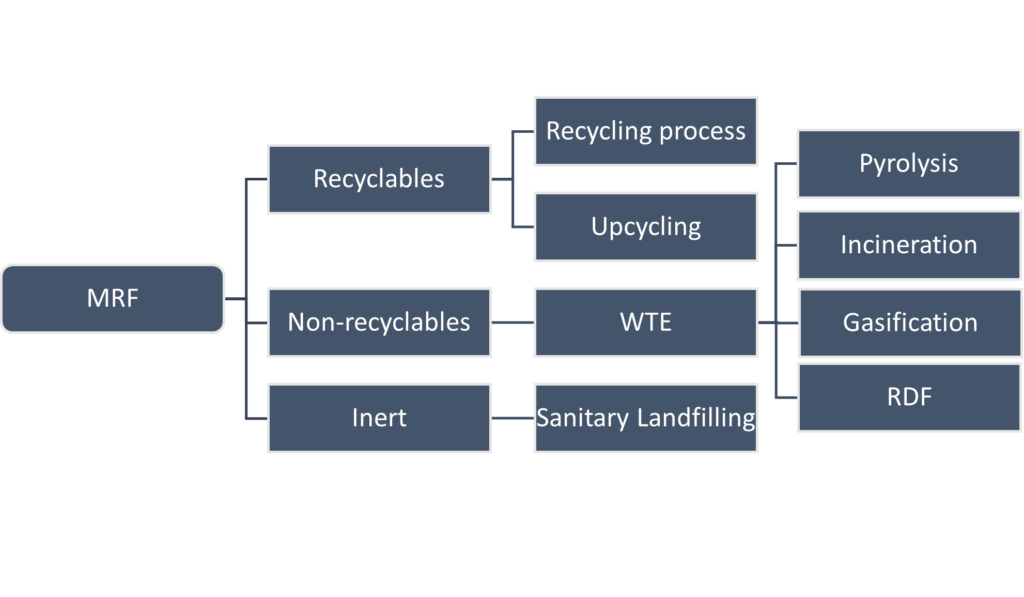
Material Recovery Facilities (MRFs) are specialized facilities that separate, process, and prepare recyclable materials for market. They use various techniques like shredding, sorting, and screening to separate different types of recyclables.
MRFs are facilities where mixed dry waste is sorted and separated into different categories using various technologies such as magnets, screens, and air classifiers. The technical guidelines for material recovery facilities include setting up the facility in a designated area, ensuring proper ventilation, providing safety equipment for workers, and maintaining a record of the amount and type of waste processed.
A few technical guidelines for MRFs in India
In India, the guidelines for setting up Material Recovery Facilities (MRFs) are provided by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- Location: MRFs should be set up in designated areas that are easily accessible by waste collection vehicles.
- Design and layout: The design and layout of the MRF should be such that it allows for efficient sorting and separation of waste. The facility should have separate areas for storage of different types of waste, sorting and processing equipment, and a loading/unloading area for waste collection vehicles.
- Equipment: The MRF should be equipped with suitable machinery and equipment for sorting, shredding, baling, and storing of waste. The equipment should meet the required safety standards and should be maintained regularly.
- Capacity: The minimum capacity for an MRF in India is 1 ton per day, while the maximum capacity varies from state to state. However, the CPCB recommends that the capacity of the MRF should be determined based on the quantity and type of waste generated in the area.
- Workers: The MRF should have adequate numbers of trained workers to operate the equipment and handle the waste. The workers should be provided with appropriate safety equipment and training on handling hazardous waste.
- Environmental considerations: The MRF should comply with all the relevant environmental regulations, including those related to air and water pollution, noise levels, and disposal of hazardous waste.
Overall, the guidelines for MRFs in India aim to promote safe and efficient handling of waste, reduce the amount of waste going to landfills, and promote the recycling of materials.
Types of Material Recovery Facilities
There are several types of Material Recovery Facilities (MRFs) in India, each with its own waste handling capacity and resource requirements. Here are some examples:
- Manual Sorting MRF: This type of MRF involves manual sorting of waste, and can handle up to 1-10 tonnes of waste per day. The resource requirements for this type of MRF include a sorting shed, conveyor belts, hand gloves, masks, and other protective gear for workers.
- Semi-Mechanized MRF: A semi-mechanized MRF uses a combination of manual and mechanical sorting to process waste. It can handle up to 20-50 tonnes of waste per day. The resource requirements for this type of MRF include a sorting shed, conveyor belts, manual and automatic waste segregation machines, and safety equipment for workers.
- Fully Mechanized MRF: A fully mechanized MRF uses advanced technology such as magnetic separators, eddy current separators, and optical sorters to sort waste. It can handle up to 100-150 tonnes of waste per day. The resource requirements for this type of MRF include a sorting shed, conveyor belts, advanced sorting machines, and trained technicians to operate and maintain the equipment.
- Integrated Waste Management Facility: An Integrated Waste Management Facility (IWMF) is a large-scale waste processing plant that combines several waste management technologies such as MRFs, composting, waste-to-energy, and landfilling. It can handle up to 500-1000 tonnes of waste per day. The resource requirements for this type of facility include a large area of land, advanced waste management technologies, skilled technicians, and significant investment.
In terms of resource requirements, the guidelines for MRFs in India emphasize the need for adequate infrastructure, equipment, safety measures, and trained personnel. The Solid Waste Management Rules 2016 require that MRFs should have proper infrastructure, including sorting sheds, storage facilities, and safety equipment for workers.
The rules also require that MRFs should maintain records of the amount and type of waste processed and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. It is essential to conduct a detailed feasibility study before setting up an MRF to determine the appropriate technology and resource requirements based on local conditions and requirements.
